Random Matrix Theory and the Riemann Zeta Function
Abstract
Undergraduate (BSc) research project concerning one of the most renown concepts in Mathematics. The Riemann zeta function is widely used in all scientific fields, however, one baffling problem is yet to be solved. In 1859, Bernhard Riemann would propose a hypothesis that would remain unsolved and frustrate mathematicians for years to come. The importance of the Riemann hypothesis is given by its connection to the nature of prime numbers and their distribution.
This paper is an exposition on the recent research made by Keating, Jon P., and Nina C. Snaith, on the connection between the distribution of the spacing between consecutive (ordered) eigenvalues of random matrices and the spacing distribution between consecutive zeros of the Riemann zeta function.
Quick Look
A random matrix is generally defined as a matrix with random variables as some or all of its entries. For instance, given x1,x2,...,x6~𝒟(μ, σ2), where μ and σ2 are respectively the mean and variance of a probability distribution 𝒟, X is a random matrix
Random matrices have various applications in nuclear physics, quantum chaos theory, number theory, etc..
One of its applications in nuclear physics was postulated by Eugene Wigner, where he surmised that the behaviour of energy levels in a simple sequence is identical to that of the eigenvalues of a random matrix. From that, we get the Wigner surmise (pg. 20), which generalises the probability density function for the spacing of the eigenvalues of a Hermitian (pg. 11) random matrix.
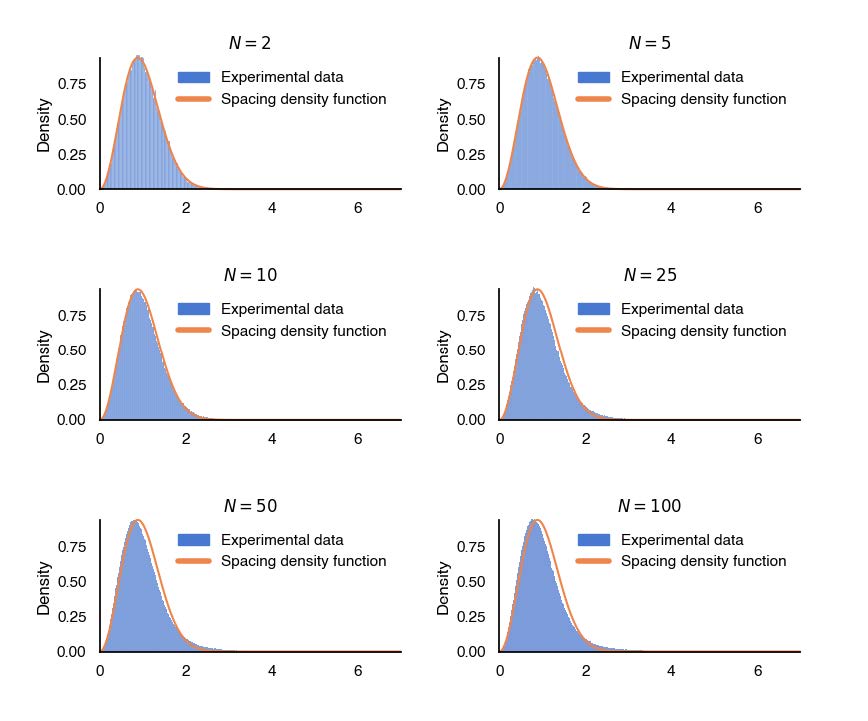
Hence, this sets the foundation for this thesis in regards to the conjecture formulated by Keating, Jon P., and Nina C. Snaith (pg. 24), where we can find a connection between the characteristic equation of a random matrix from the circular unitary ensemble (CUE) and its k-th moment.
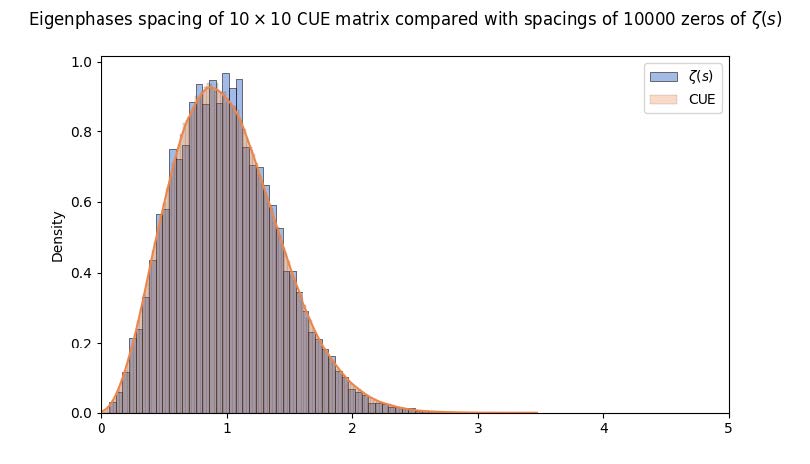
More specifically, we observe that the logarithm of the characteristic equation of a random matrix from the CUE approaches a Gaussian distribution and assumes the analytic properties of the Riemann zeta function.
Errata
Take caution in reading pages 22 and 23. The explanation and visualization are not correct. Read this for the correct definition.
